“Adoption, Fragility and Regulation of Stablecoins”, SUERF Policy Brief No. 662, August 2023.
“Federal Reserve Speeches Meet Transformer Models” with Isaiah Hull, Robin L Lumsdaine, and Xin Zhang, SUERF Policy Brief No. 528, February 2023.
“Wake-Up Call Contagion” with Toni Ahnert, SUERF Policy Brief No. 385, July 2022.
“Hedging against exchange rate risk – maturity choice and roll-over risk”, The Sveriges Riksbank Economic Review 2022:1, March 2022.
- Abstract: The Swedish market for hedging foreign exchange (FX) risk is about double the size of the annual Swedish gross domestic product. Key buyers of FX risk protection are Swedish insurance companies and pension funds who regularly invest in foreign currency assets, which exposes them to exchange rate risk. The dominant sellers of FX risk protection are Swedish banks. The most commonly used financial instruments are FX swaps with a duration of 3 months or less. Since the typical investment horizon of insurance companies or pension funds can span multiple years, shorter-term FX hedging arrangements need to be rolled over repeatedly. In this article, we offer a conceptual framework to discuss the risks and benefits associated with short-term hedging for six risk categories: FX risk, asset price risk, FX market distress, premature liquidation risk, counterparty risk and inflation risk. The focus is on economic considerations that have to do with uncertainty and information.

Decomposition of the maturity profile of the nominal outstanding FX hedging contracts in the Swedish market. 2020 averages for the remaining maturity calculated over the end-of- month values.
- Keywords: FX hedging, financial stability.
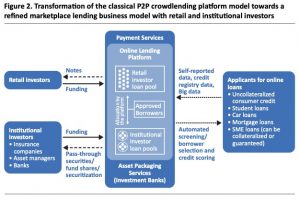
“FinTech credit: Online lending platforms in Sweden and beyond” with Carl-Johan Rosenvinge (Sveriges Riksbank), The Sveriges Riksbank Economic Review 2019:2, October 2019.
- Abstract: New digital technologies in banking and finance, commonly referred to as ‘FinTech,’ have the potential to transform established banking business models. This article studies online lending platforms, which are new players in the financial sector that allow individuals or firms to obtain loans directly from investors via the internet. To date, online lending is still small relative to total bank lending. However, online lending has expanded rapidly not only in China, the US and the UK, but also in Sweden. In 2018 Swedish platforms originated more than SEK 2bn of new loans – exceeding the 2017 volume by 51 per cent. We discuss how online lending platforms differ from commercial banks and how they are regulated. Moreover, we analyse market developments, such as the growing linkages between platforms and the banking sector. Against this backdrop, we review potential financial stability implications that may appear if online lending continues to grow in importance.
- Keywords: FinTech credit, financial stability.
“Revisiting the role of central banks as liquidity providers – old and new challenges” with Johan Molin (Sveriges Riksbank), The Sveriges Riksbank Economic Review 2016:2, September 2016.
- Abstract: This article offers a review of the role of central banks as providers of public liquidity. Against the backdrop of the global financial crisis of 2007-2009, we discuss various challenges for public liquidity provision and the effectiveness of central bank lending facilities. These challenges help us identify potential gaps in existing mechanisms and frameworks governing liquidity assistance. We discuss how the available liquidity policy tool kit can be used to deal with the challenges. Furthermore, we highlight modifications to existing central bank facilities during and after the global financial crisis. We point at trade-offs faced by policy makers and describe potential pitfalls for public liquidity providers. Lastly, we attempt to look ahead and outline some specific challenges posed by more recent structural, regulatory, and technological developments in the financial system.
- Keywords: central bank liquidity assistance, liquidity provision, liquidity policy, Great Financial Crisis.
Contribution to reports
I was a member of the Committee on the Global Financial System (CGFS) Working Group on Policy Challenges and Open Issues in Liquidity Assistance, which produced a report on “Designing frameworks for central bank liquidity assistance: addressing new challenges”, CGFS Papers No 58, April 2017.
Disclaimer: This is my private homepage and the views expressed are my own.